Understanding the Bone Graft Process for Dental Implants
What is a Bone Graft in Dental Implants?
When it comes to dental implants, the success of the procedure often depends on the strength and density of the jawbone. A bone graft is a procedure that helps to rebuild or regenerate bone in areas where it has been lost or weakened. This process is crucial for patients who have insufficient bone structure as it provides a solid foundation for dental implants.
The bone graft material can come from various sources, including the patient's own body, a donor, or synthetic materials. The choice of material depends on individual needs and the specific situation. Understanding the bone graft process is essential for anyone considering dental implants.
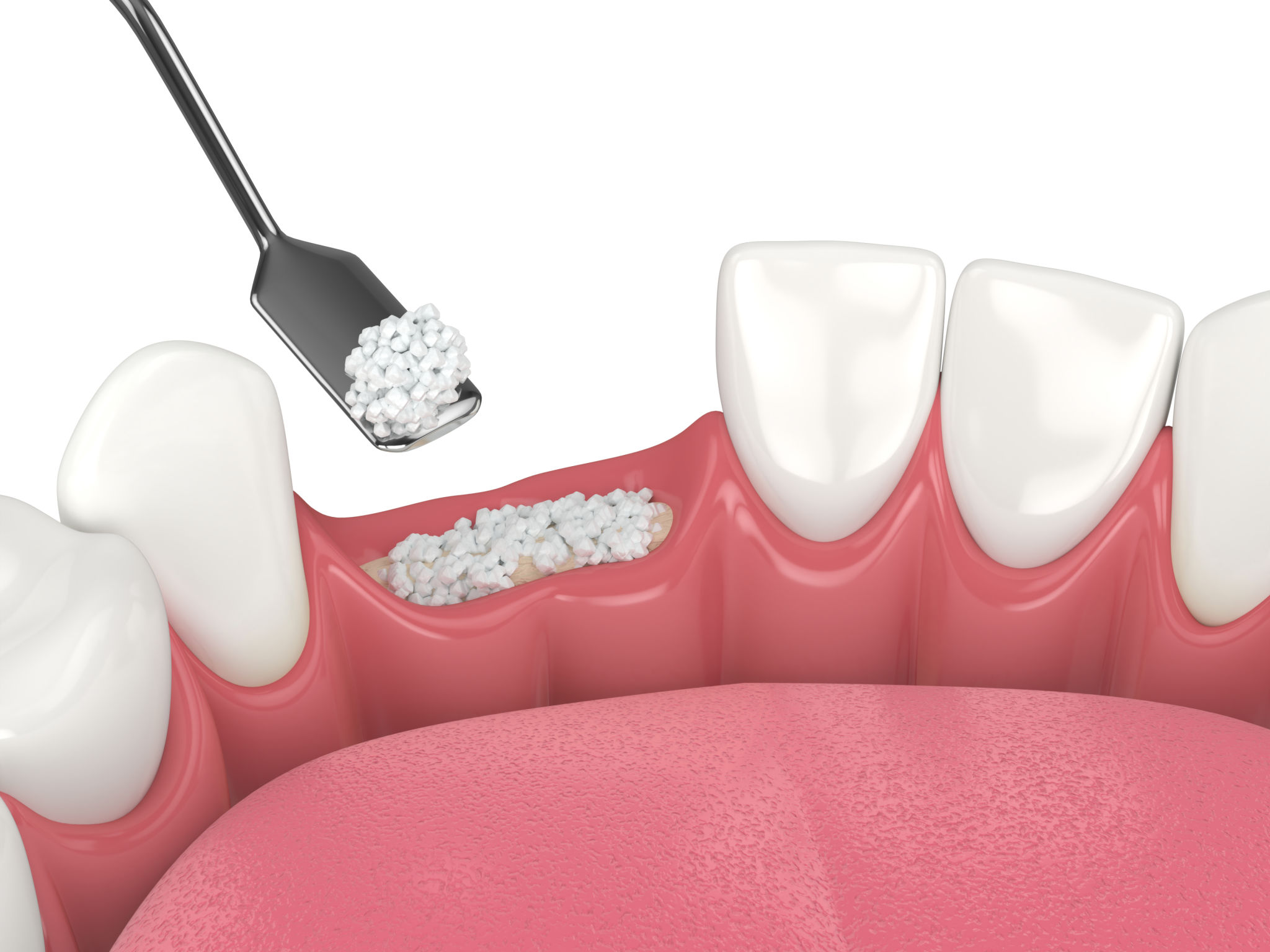
Why is a Bone Graft Necessary?
Bone grafts are often necessary because of bone loss, which can occur for several reasons, such as tooth loss, periodontal disease, or trauma. When a tooth is missing, the jawbone in that area can begin to deteriorate over time. This can lead to an inadequate bone structure for supporting a dental implant.
By performing a bone graft, dentists can ensure there is enough bone mass to secure the implant firmly. This not only increases the success rate of the implant procedure but also helps maintain the natural contour of the face and jaw.
The Bone Graft Procedure
Initially, the dentist will conduct a thorough examination, including X-rays or CT scans, to assess the condition of the jawbone. If a bone graft is required, the dentist will discuss the best type of graft material to use and explain the procedure in detail.
The procedure involves making a small incision in the gum to access the jawbone. The graft material is then placed in the area where bone is needed. Over time, the graft integrates with the existing bone, promoting new bone growth.
Types of Bone Graft Materials
There are several types of bone graft materials available:
- Autografts: Bone taken from another part of the patient's body, usually the hip or chin.
- Allografts: Bone sourced from a donor.
- Xenografts: Bone taken from an animal source, like bovine.
- Alloplasts: Synthetic materials designed to mimic bone structure.
Recovery and Healing
After the bone graft procedure, it is vital to follow the dentist's post-operative care instructions to ensure proper healing. The recovery period can vary depending on the type of graft material used and the individual's overall health. Generally, it takes several months for the graft to integrate fully with the existing bone.
During this time, patients may experience some discomfort or swelling, which can typically be managed with prescribed medications. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the healing process and determine when the site is ready for the dental implant.

Benefits of Bone Grafting for Dental Implants
Undergoing a bone graft offers several advantages. It significantly increases the likelihood of successful dental implant placement. A stable and robust bone structure ensures the implant remains secure and functions like a natural tooth.
Moreover, bone grafting helps prevent further bone loss and maintains the integrity of the jawline and facial structure. This can have positive effects not only on oral health but also on the overall appearance and confidence of the patient.
Conclusion
Understanding the bone graft process is vital for anyone considering dental implants. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the procedure's success and the long-term health of the implant. If you're facing bone loss or considering dental implants, consult with your dentist to explore the best options for bone grafting and ensure a successful outcome.
